Acute Sinusitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
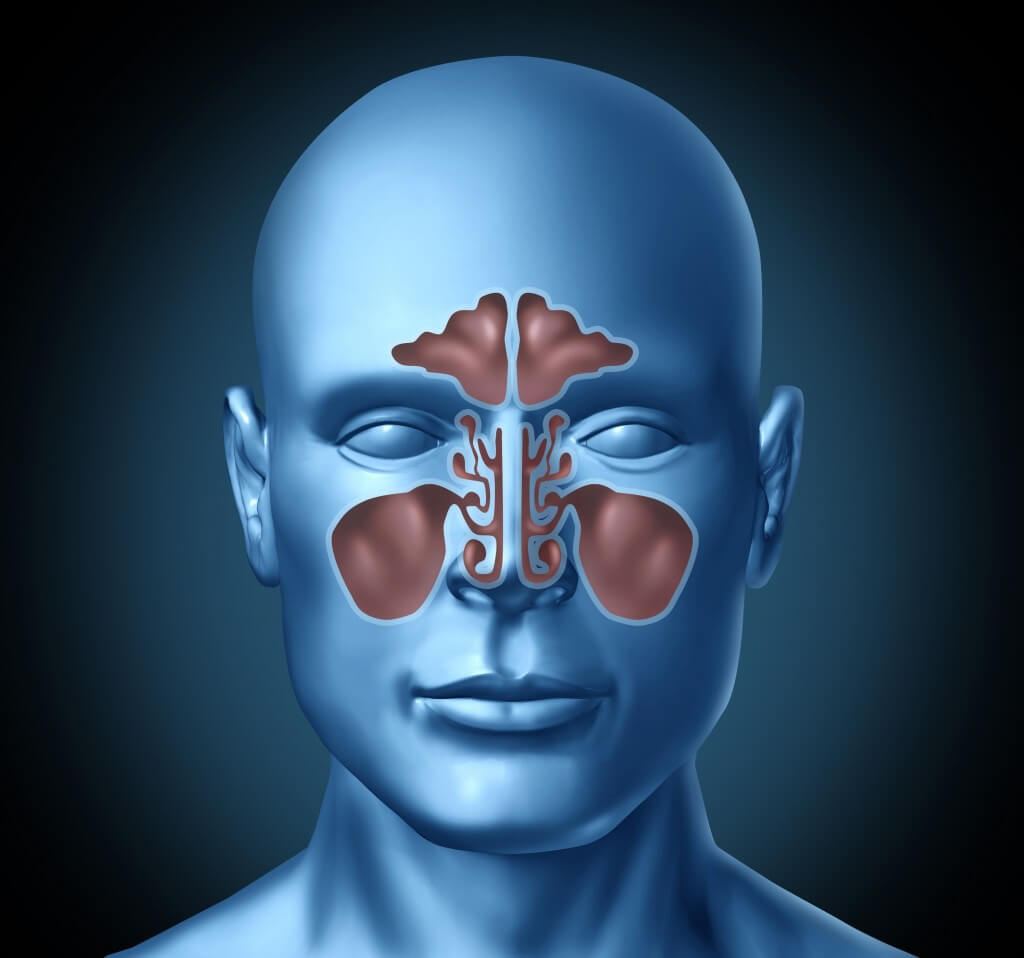
Acute sinusitis, also known as acute rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation in the sinus cavities which prevents the drainage of mucus from sinus passages. Although the symptoms of acute sinus typically last for a few week, in subacute cases, the issues may persist for more than a month. Leading the conversation further, in this blog post, we discuss the risk factors, symptoms and treatment methodologies of acute sinusitis. Let’s begin.

Causes and Catalysts
Common cold, seasonal flu or allergies are some the most common factors that trigger acute sinusitis. Most cases of acute sinusitis begin as common cold and the symptoms go away within a week. Some people, however, may develop the symptoms of bacterial infection.
The following factors may increase the risk of developing acute sinusitis:
- Hay fever and allergies
- Disease affecting cilia function such as Kartagener Syndrome
- Continuous exposure to a contagious environment
- A weak immune system
- Nasal polyp or deviated septum
- Smoking or breathing in pollutants
In addition to these factors, medical procedures such as inserting a nasogastric tube from the nose to the stomach can also pose a risk of developing acute sinusitis, albeit in rare cases.
Symptoms
Pain and Sensitivity in the Sinus Area
Acute sinusitis results in a pulsating, throbbing pain over the infected sinus area. The pain worsens while bending the head forward and chewing is painful.
Nasal Symptoms
Blocked Nose
The patient experiences stuffiness in one or both the nasal passages, along with temporary smell loss in rare cases.
Runny Nose
A runny nose along with a green/yellow discharge indicate a microbial infection as a result of acute sinusitis. If the sinus discharge channels get blocked with thick mucus, a runny nose may dry up and increase the tenderness and pain over the infected sinus area.
In addition, other symptoms of acute sinusitis include headaches, toothache, cough, bad breath, tiredness and pressure or fullness in the ears.
Treatment Options
Most symptoms of acute sinusitis subside within a few weeks. Typical treatments include:
Antibiotics
Your ENT doctor may prescribe antibiotic tablets or capsules to treat bacterial sinus infections with a medication period of a few weeks.
Painkillers
Over-the-counter painkillers such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Advil, Tylenol or Motrin can ease up the infected sinus pain. To avoid complications or side effects, it might be essential to take a painkiller or oral medication after consulting an ENT specialist.
Nasal Sprays and Decongestants
While nasal sprays such as Flonase or Nasonex are prescribed to reduce sinus inflammation, decongestants such as Sudafed and Actifed are prescribed to dry up the mucus.
Nasal Cleaners
Cleaning the inside of the nose with saline sprays reduces nasal congestion and discharge relieving the symptoms of sinusitis.
Warm Packs
Applying warm packs on the infected sinus area helps in draining the mucus-clogged sinuses and provides relief from sinus pain.
Must Read: Balloon Sinuplasty: An Effective Remedy for Chronic Sinusitis and Recurrent Acute Sinusitis
The Way Forward
Acute sinusitis, if ignored for long enough, may aggravate into chronic sinusitis that has various serious health implications requiring immediate medical attention. Therefore, if cold and allergy symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, it becomes essential to consult an ENT specialist. If you or someone you know has been experiencing any of the symptoms discussed in the post, feel free to get in touch with us for expert consultation.

